Chapter 02 : What is Blockchain?
Understanding
Blockchain
Introduction: Blockchains are essentially decentralized databases that are spread out across a network of peers. This implies that no single individual or entity controls the network. Instead, computers worldwide collaborate to establish a reliable ledger of transactions that is accessible and verifiable by anyone.

In a blockchain, information is organized into “blocks.” These blocks are linked together in chronological order, creating what can be thought of as a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
Each block consists of three key components:
-
Transaction data: This includes details such as the sender, recipient, amount transacted, and the timestamp of the transaction. Transection Data Example:1
- Sender: JohnDoe123
- Recipient: JaneSmith456
- Amount: 0.05 BTC
- Timestamp: January 15, 2024, 10:30 AM
In this example, JohnDoe123 is sending 0.05 BTC to JaneSmith456, and the transaction occurred on January 15, 2024, at 10:30 AM. This information is recorded within a block on the blockchain and can be viewed and verified by anyone on the network.
-
A cryptographic hash: This is a unique alphanumeric code used to identify the data contained within the block. Any alteration to the data in the block will result in a change in the hash value.2
-
A cryptographic hash of the previous block: Whenever a new block is added to the blockchain, it includes a reference to the previous block's unique hash. This creates a sequential link between blocks, ensuring the integrity and continuity of the blockchain's history. The only exception is the initial block in the chain, known as the 'genesis block,' which does not reference a previous block since it is the first one.3
-
How exactly do blockchains operate?: To ensure trust and verification of data across the network, blockchains rely on a consensus mechanism. This mechanism dictates how agreement is reached among network participants. The most common method, utilized by cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, is Proof of Work (PoW). However, an increasingly popular alternative is Proof of Stake (PoS), which Ethereum is set to transition to with the advent of ETH 2.0. Here's a breakdown of how these consensus mechanisms function:4
-
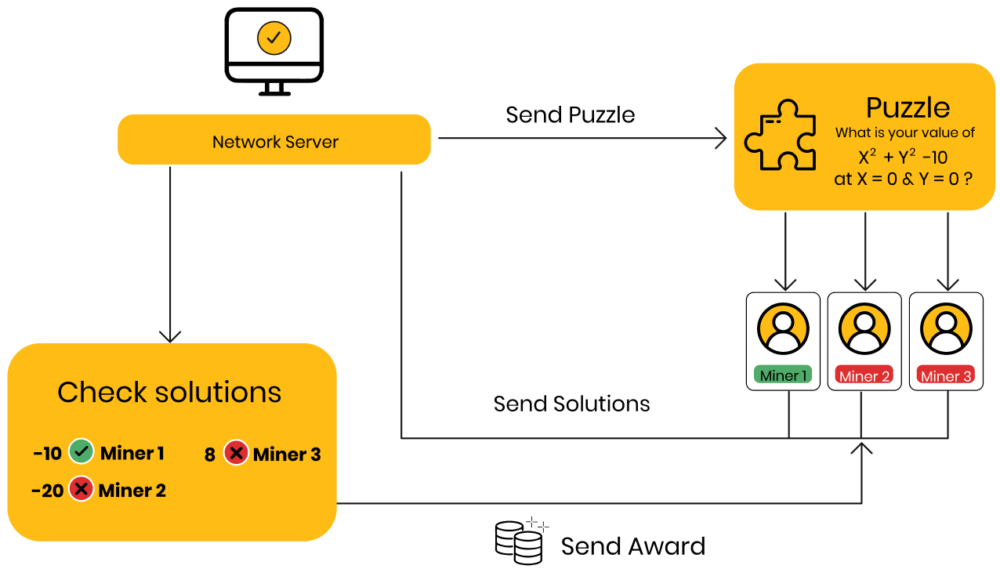
Proof Of Work: In the Proof of Work mechanism, specialized computers referred to as "miners" engage in solving complex cryptographic puzzles to generate new blocks. The miner who successfully solves the puzzle first then shares the solution with other participants on the network. Once a consensus is reached among the network's miners that the solution is valid, a new block is appended to the blockchain. As an incentive for their efforts, the miner who solved the puzzle receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency, along with any transaction fees associated with the transactions in that block.
-
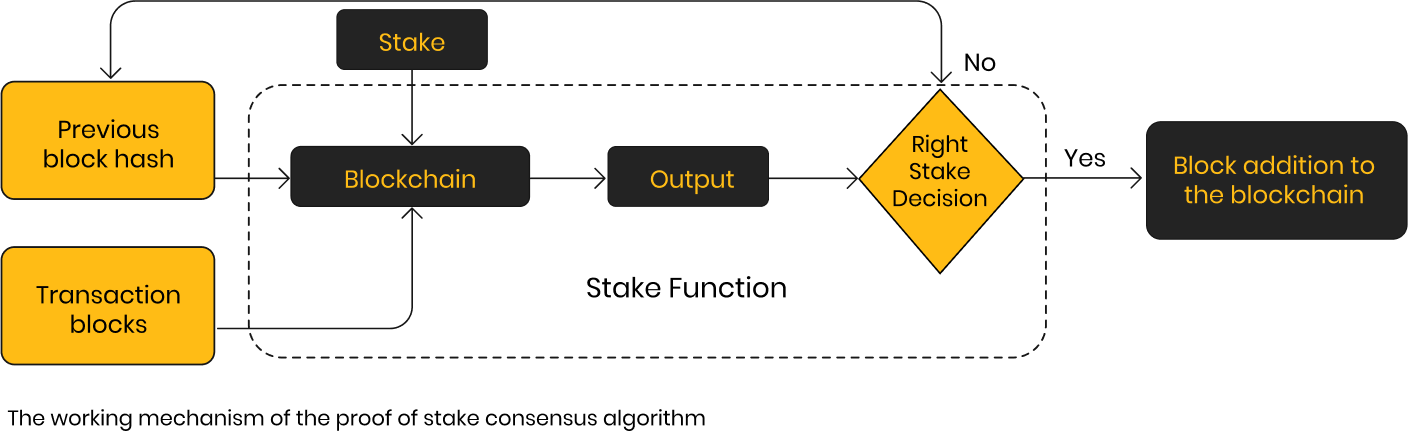
Proof of Stake (PoS) : In the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, rather than relying on miners, the system employs randomly chosen validators. These validators are individuals who commit a portion of the blockchain's native cryptocurrency, known as "staking," to validate and generate blocks. By staking, validators are effectively bound to the blockchain, and any negligent or malicious behavior results in a reduction of their staked amount through slashing penalties.Top of Form
What benefits does blockchain technology offer?
Blockchain technology offers a multitude of advantages. Here are several:
- Permissionless: Individuals from any location can freely send cryptocurrency to recipients with wallets, without any authority having the ability to intervene or restrict transactions.
- Privacy: Blockchain transactions do not require personal identification, ensuring a level of anonymity and privacy for users.
- Autonomy: Users maintain complete control over their funds, without the need for intermediaries or third-party entities to manage transactions.
- Decentralization: Blockchains operate on a distributed network, eliminating the risk of a single point of failure that could disrupt the entire system. This decentralized nature ensures resilience and security across borders and jurisdictions.

Chapter 01 :
What is Web3?
In recent years, there has been growing talk about Web3 and its potential to revolutionize the internet as we know it.

Chapter 03 :
What is Cryptocurrency ?
Cryptocurrency has become a buzzword in recent years, revolutionizing the way we think about money and finance.

