Chapter 05 : What is Proof Of Work?
Understanding
Proof of Work
(PoW) in Blockchain Technology

What are Crypto Tokens? :
Crypto tokens are digital assets that are issued and transferred on a blockchain platform. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which operate on their own independent blockchains, tokens are created on existing blockchain networks, leveraging their infrastructure and protocols. Tokens can represent a wide range of assets, rights, or utilities, and their value is determined by market demand and the underlying network’s dynamics.
-
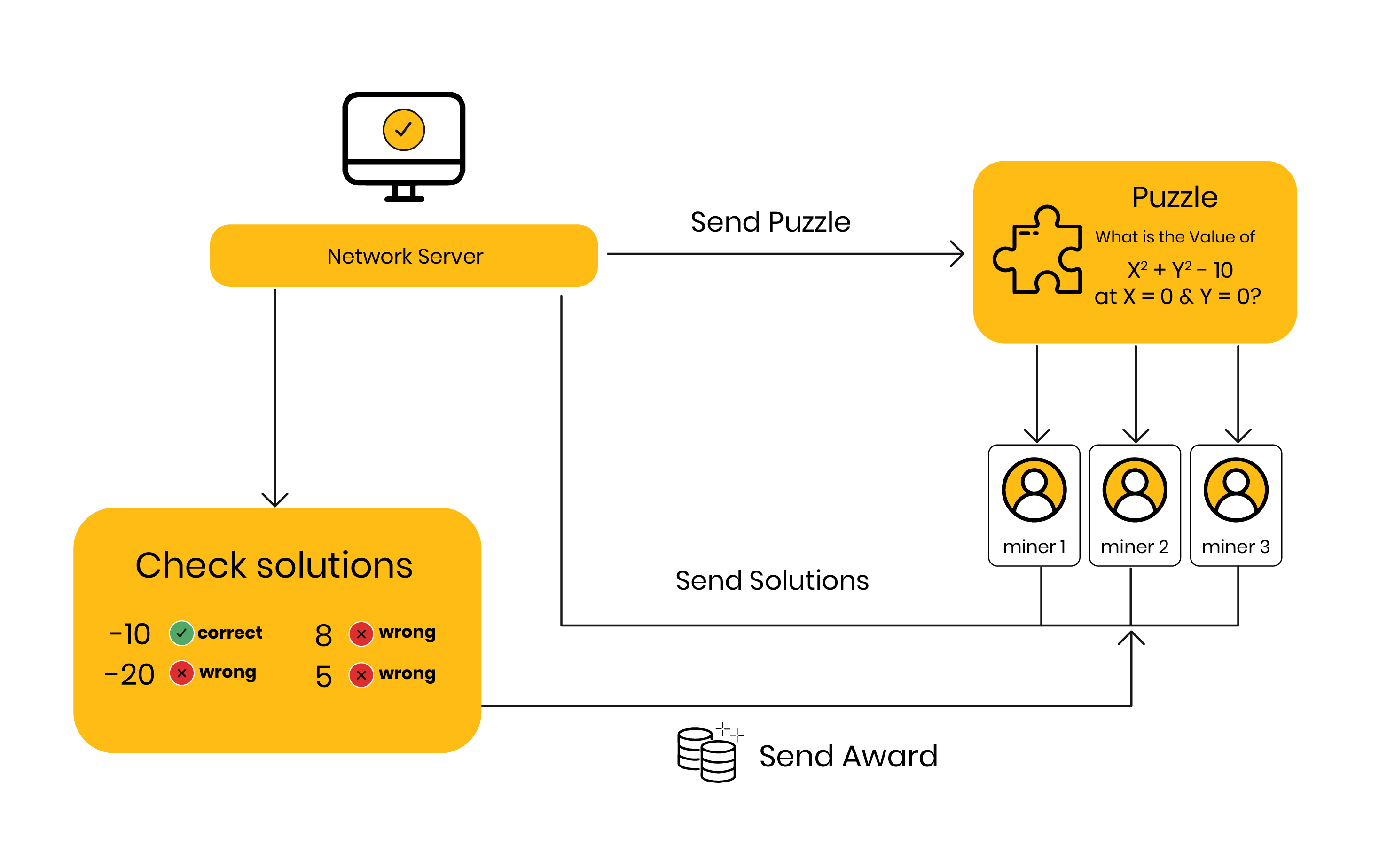
Definition of Proof of Work:1
- Proof of Work is a consensus algorithm used in blockchain networks to confirm and validate transactions.
- It requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks of transactions to the blockchain.
- The process of solving these puzzles consumes computational resources and energy, demonstrating that the miner has performed a certain amount of work.
-
How Proof of Work Works:2
- Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles by using computational power to find a hash value that meets specific criteria.
- The puzzle typically involves finding a nonce (a random number) that, when combined with transaction data, produces a hash value below a certain target threshold.
- Miners repeatedly hash different nonce values until one of them discovers a valid solution.
- Once a miner finds a valid solution, they broadcast it to the network, and other nodes verify its correctness.
- The first miner to solve the puzzle and validate the block receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin.
-
Significance of Proof of Work:3
- Security: Proof of Work ensures the security and integrity of the blockchain network by making it computationally expensive to alter past transactions.
- Decentralization: By distributing the task of block validation among miners, Proof of Work promotes decentralization and prevents any single entity from controlling the network.
- Incentives: Miners are incentivized to participate in the network through block rewards and transaction fees, which helps sustain the blockchain ecosystem.
- Trustless System: Proof of Work enables trustless transactions, where participants can interact and transact with each other without relying on a central authority.
Conclusion: In summary, crypto tokens play a crucial role in the digital economy, offering a versatile and efficient means of representing assets, rights, and utilities on blockchain networks. Understanding the different types of tokens and their respective use cases is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.

Chapter 04 :
What are Crypto Tokens?
Cryptocurrency tokens have become an integral part of the digital economy, offering unique functionalities and use cases within blockchain .

Chapter 06 :
What is Ethereum ?
At its core, Ethereum is a blockchain-based platform that facilitates peer-to-peer transactions and the execution of smart contracts.

